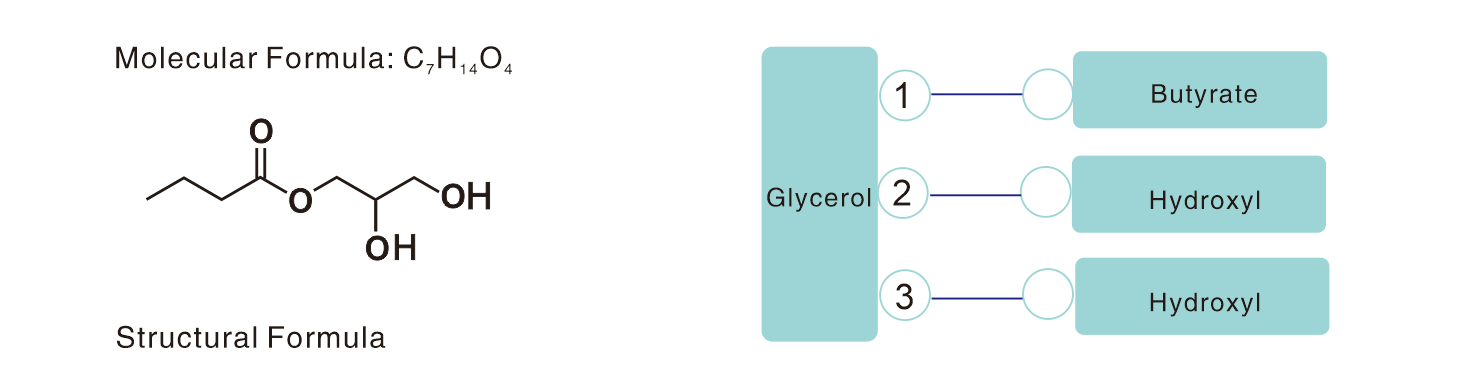
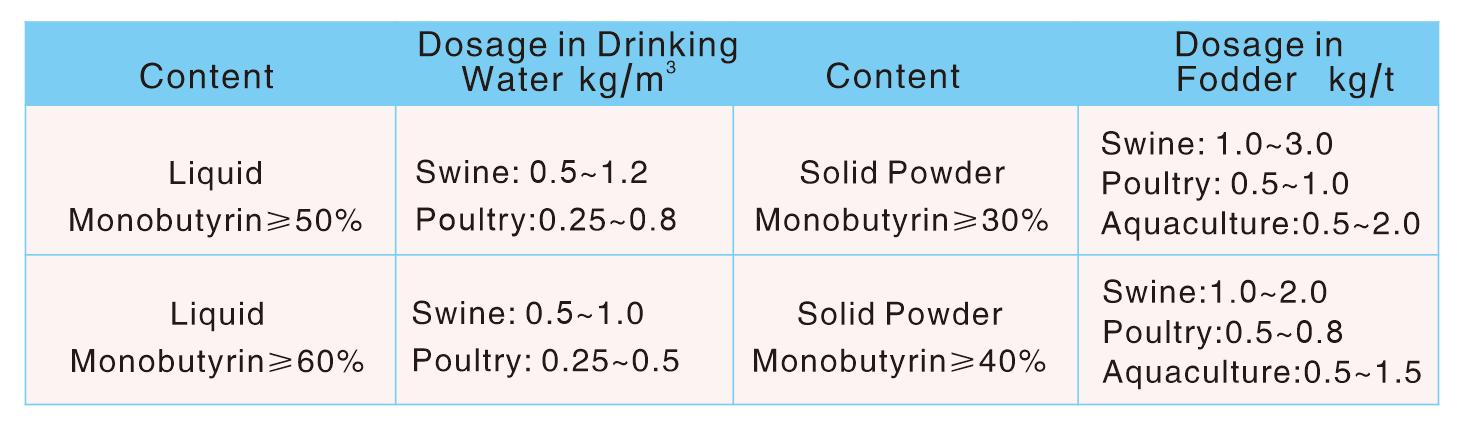
Monobutyrin (45%, 50% )
Monobutyrin(Glycerol Monobutyrate or GMB),as an kind of derivative of butyrate,it is synthesized by esterification of butyric acid and glycerol. It is fully soluble in water,odorless and passing through stomach in the form of glycerides.During animals production,it behaves as hematopoiesis bacteriostasis,promotion of intestinal development and oil emulsification,enhancing the digestion and absorption of animal nutrients,improving the growth performance and health etc.



 027-65692519
027-65692519