 Sendtime:2020-06-14
Sendtime:2020-06-14
 Pageviews:513
Pageviews:513
Feed intake known as a vital activity for animals to survive, while a more sufficient feed intake is a necessity to release animals’ production potential. Feed intake is affected by varieties of elements , which includes environmental factors, animal factors, feed factors and etc.. Stress reaction happens inevitably on animals is caused by feed changing, cold and hot stimulation, being manic and bellicose that driven by estrus during production practice, which will lead to a negative affection to production efficiency. In recent years, attention has been paid to the research on the regulation of feed intake of animals. The main method is to add exogenous additives, promoting feed intake through neuroregulation and humoral regulation. According to some reports, the γ-Amino butyric acid (GABA) has a physiological function that covers feed intake promotion, anti-stress and sedation on animals.
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter wildly exists inside mammals. The academic community has done numerous studies on feeding GABA in animal diets to fight stress reaction and improve feed intake.
Overview of GABA and its physiological functions
GABA, also known as aminobutyric acid, is the product of glutamic acid (Glu) under the action of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) by the -decarboxylation reaction. GABA is an important inhibitory amino acid neurotransmitter in central nervous system, and it has different modes of action in different parts. GABA’ mode of action in brain is dominated by post-synaptic inhibition, while it is dominated by presynaptic inhibition in medulla.
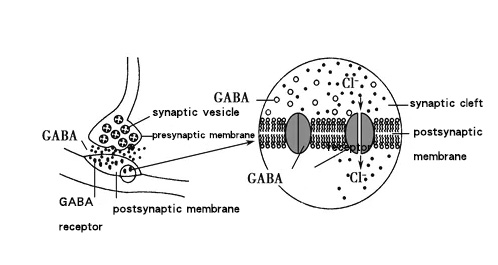
The physiological functions of GABA are mainly reflected in its regulation of normal physiological functions of the body, which includes blood pressure reduction, nerves sedation, cell’s anti-aging and anti-stress. In addition, GABA has an obvious regulatory effect on feed intake in animals.
Mechanism of improving feed intake
The mechanism of GABA regulating feed intake has been widely reported. Now we will introduce you the most recognized 3 ways of all.
1. Inhibiting satiety centers
The satiety center is located in the ventromedial hypothalamus nucleus (VMH). The body sends messages to VMH by sensing glucose levels in blood and hypothalamus, then the satiety nerve regulates feed intake. GABA is a signaling molecule in VMH that promotes feed intake. When glucose is deficient, the concentration of GABA in VMH will increase, which leads to an increase in feed intake.
2. Through function of taste
There are three subtypes of taste receptor cells (TRCs). The taste reflection functions through message transmission that happens among the three subtypes of taste. TRCs is dominated directly by central nervous system. Studies have shown that GABA in cells of animal taste buds involves in taste regulation, meantime, a microinjection of GABA into the medial medulla oblongata of animals will increase its feed intake as well.
3. Synergies with NPY
NPY is called neuropeptide tyrosine. In central nervous system, NPY has various biological functions, such as promoting animal feed intake, affecting hormone secretion, sexual behavior, and temperature regulation etc.. With a series of signal transmission occurs among NPY neurons , the sympathetic nerves will be inhibited and stimulated , and this triggers a strong ingestive response. GABA is a promoter to dietary effect of NPY, it promotes the secretion of NPY to increase its concentration in blood, which in turn increases the feed intake.
The mechanism of GABA to alleviate heat stress reaction
Heat stress reaction refers to the non-specific response of the body to a high temperature. Due to global warming, heat stress reaction becomes one of the most important factors to harm livestock production. Heat stress will accelerate the catabolism of fat, glycogen and protein inside the body, which causes a decreasing of feed intake and growth difficulties.
Heat stress reaction affects the production performance of livestock mainly in two ways. One is to activate the HPA axis and the inhibitory nervous system. The other is to reduce the plasma concentration of two thyroxine [triiodothylamine (T3), tetraiothylamine (T4)]and insulin,but to increase the concentration of corticosterone (CS) to affect the process of nutrient anabolism.

GABA is the main nerve antagonist in nervous system, which has the effects of anti - heat stress reaction and sedation. GABA mediates the passive action of most central and peripheral nerves. In case of heat stress reaction, dietary GABA will significantly improve animal’s weight, feed intake, weight daily gain, carcass weight, and T3 and insulin concentration in blood, as well as reduce the concentration of CS in animal blood to alleviate the effect of heat stress reaction. In addition, dietary addition of GABA will improve the activity of serum antioxidant indexes SOD and GSH-PX, reduce the activity of MDA which reflects the damage of cell membrane, and the concentration of hormones-COR, CORT and ACTH, so as to reduce the body's heat stress reaction.
Summary
In general, GABA can increase feed intake of animals by inhibiting the stimulation of satiety nerve, regulating the taste response, and promoting the secretion of NPY (an accelerant of feeding effect). Additionaly, GABA can also reduce stress reaction by inhibiting central nervous system response and hormone secretion. Therefore, in practical production, GABA can not only inhibit stress reaction, but also promote feed intake. It’s perfectly solved the affection on feed intake caused by stress reaction, and improved the production efficiency.
With the approaching of prohibition of feeding antibiotics, while summer is on its way as well, feeding animals are bound to face a variety of stress reaction, such as high humidity and heat, no antibiotics in feed, environmental microorganisms increasing etc., then GABA will be your best option to improve production efficiency.
Application solution
Dosage recommendation of GABA
|
Animal Species |
Dosage (100%) |
|
Pig |
50-100g/t |
|
Poultry |
50-150g/t |
|
Ruminants |
0.6-1.2g/head /day |
|
Aquatic animals |
100-150g/t |